Fibrosis occurs due to the excessive production and accumulation of collagen and other extracellular matrix proteins in tissues and organs. This leads to increased tissue scarring, contributing to a range of diseases, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), cirrhosis, chronic kidney disease (CKD), myocardial infarction, heart failure, celiac disease, scleroderma, diabetes, and others. At Aragen, we provide a comprehensive portfolio of preclinical in vivo fibrosis models across multiple organs, supported by in vitro and ex vivo assays, histology, and AI-powered digital pathology solutions.
With nearly two decades of expertise, we have conducted hundreds of studies to evaluate the efficacy of test compounds across various modalities, including small molecules, biologics, RNA therapeutics, peptides, and exosomes. Our work has played a pivotal role in supporting successful IND submissions for our clients, with several current programs in clinical development.
In Vivo Fibrosis Models
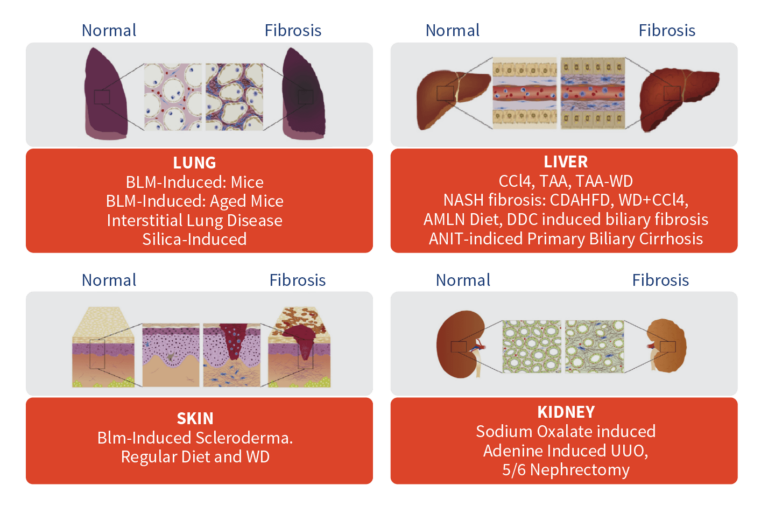
Aragen offers a wide selection of in vivo fibrosis models across various organs, along with customized fibrosis models tailored to specific research needs. Our models are designed to support the investigation of pathways and mechanisms involved in fibrosis, as well as the development of effective treatments.
Why Aragen?
- Strong track record: Established in 2008, our Fibrosis program has earned a strong reputation in the industry for conducting high-quality, impactful studies.
- Comprehensive Solution: We provide more than 20 fibrosis models across multiple organs including customizable chemical-induced, diet-induced, and surgical models, all designed to accurately replicate human disease conditions.
- Advanced Analytical Tools: Benefit from cutting-edge tools such as lung function analysis using Flexivent, hypoxia-related assessments via Oximeter and ISTAT, biomarker analysis (gene expression and cytokine profiling).
- Advanced Assays and Biomarker Analysis: Our FibroPanel™ gene expression analysis allows you to link multiple fibrosis models, analyzing fibrosis-related markers (e.g., TGF-β, ECM genes, cytokines, and tissue remodeling genes) across different disease models.
- AI-Powered Digital Pathology: Our Visiopharm System enables quantitative digital pathology analysis, providing high-resolution imaging and detailed assessments of tissue morphology, collagen deposition, and inflammation, helping to accelerate your findings.